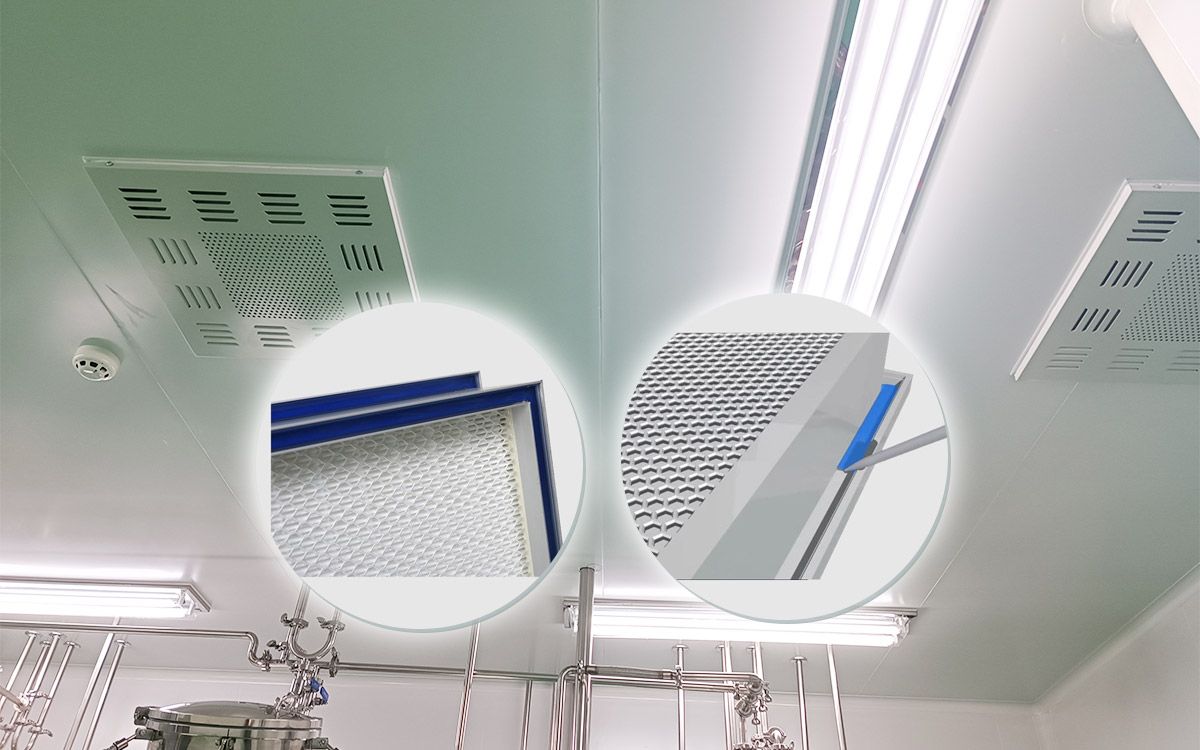
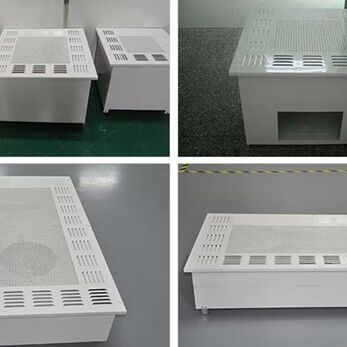
In the realm of pharmaceutical cleanrooms, maintaining a meticulously controlled environment is paramount. Here, HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters play a vital role in safeguarding product sterility by eliminating airborne contaminants.
To house these HEPA filters effectively, specialized enclosures known as HEPA boxes or filter housings are employed.
HEPA Box Fundamentals
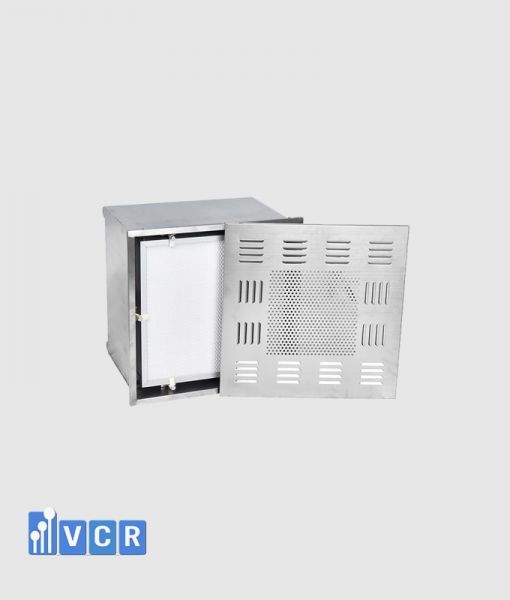
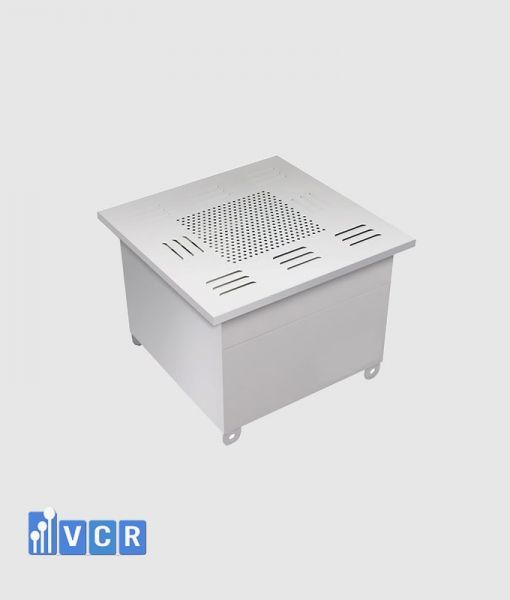
A HEPA box serves as a dedicated containment unit for a HEPA filter. It channels and directs the airflow through the filter media, ensuring optimal performance and preventing unfiltered air from bypassing the system. These enclosures are constructed from various materials, with stainless steel being a popular choice due to its durability and resistance to corrosion, a crucial factor in cleanroom environments.
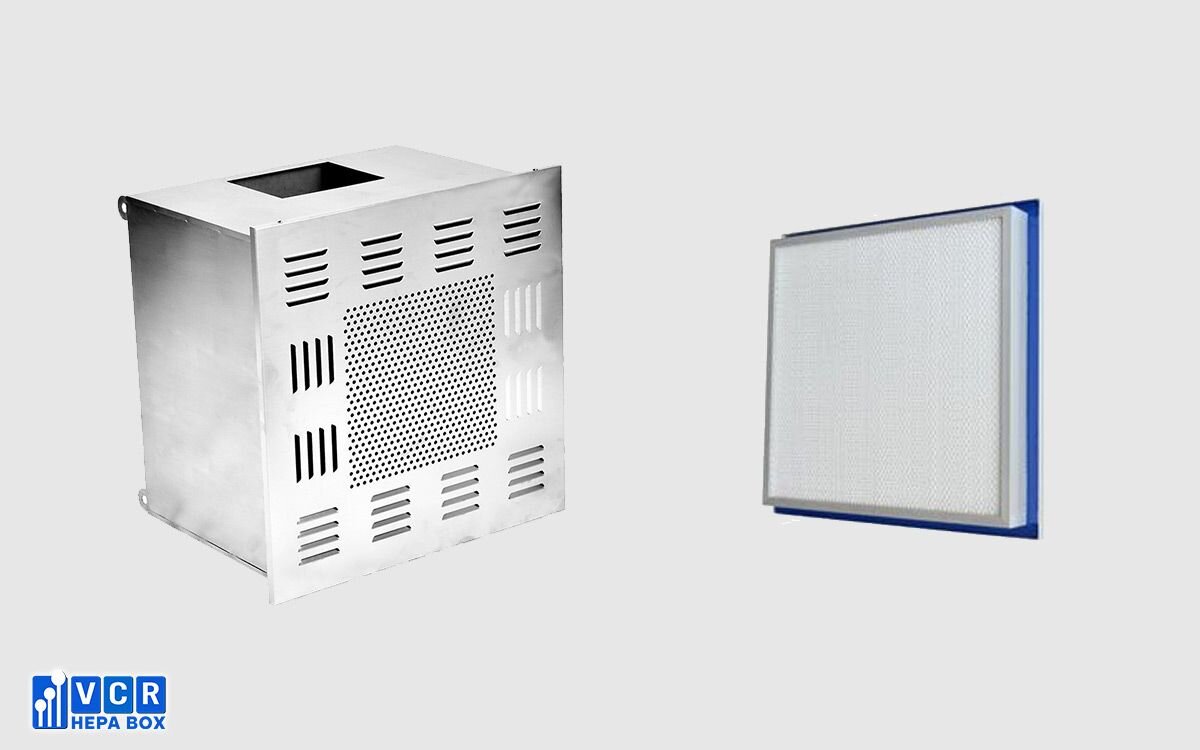
See more: HEPA Filter Terminal Box Controlled Environments
Gel-Seal Technology: A Tight Fit for Critical Applications
There are two primary sealing mechanisms for HEPA filters within their housings: gasket and gel-seal. This article focuses on gel-seal HEPA boxes, specifically designed for pharmaceutical cleanrooms with stringent air purity requirements.
Gel-Seal HEPA Boxes: Design and Functionality
Gel-seal HEPA boxes incorporate a specialized gel sealant along designated channels within the housing. This gel forms a tight, secure barrier around the filter edges, eliminating potential leakage paths for contaminated air. This superior sealing characteristic is particularly advantageous in pharmaceutical cleanrooms where even the slightest compromise in air quality can have significant consequences.
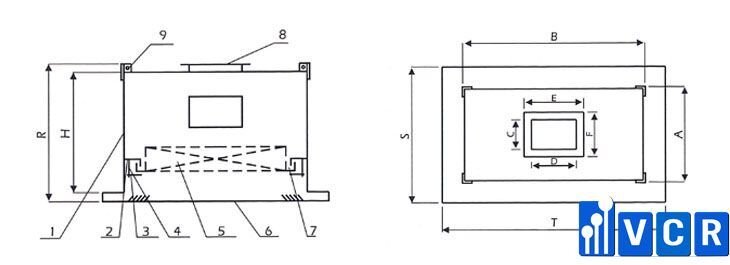
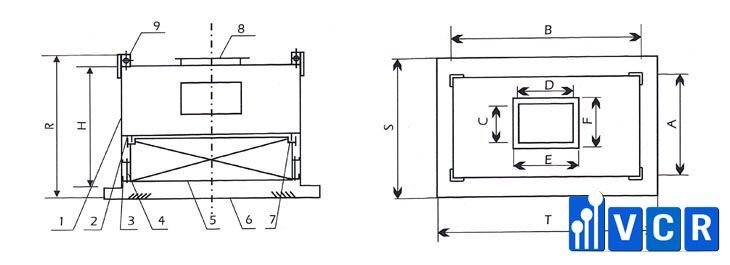
See more: The Indispensable Role of HEPA Boxes in Pharmaceutical Cleanrooms
Components of a Gel-Seal HEPA Box:
Casing: The primary structure of the enclosure, typically fabricated from stainless steel.
- Filter Housing: The compartment specifically designed to accommodate the HEPA filter.
- Positioning Clamp: A mechanism for securing the HEPA filter precisely within the housing.
- Bolts: Used in conjunction with the positioning clamp to ensure a firm and leak-proof seal.
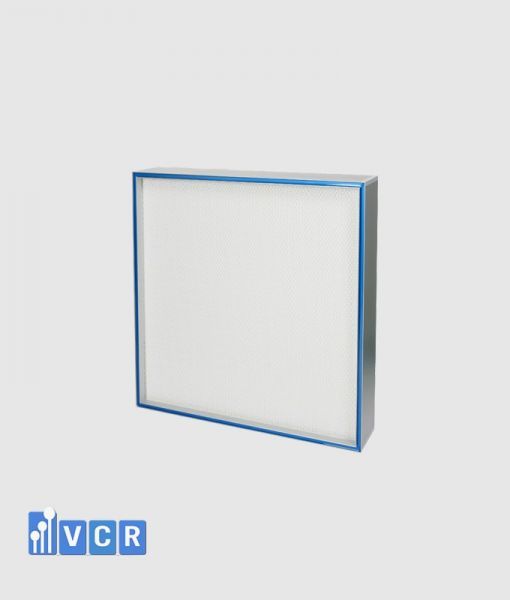
- HEPA Filter: The heart of the air filtration system, capturing airborne contaminants down to a specific size threshold (typically 0.3 microns).
- Air Diffuser (Square or Swirl Diffuser): Directs the purified airflow in a controlled pattern within the cleanroom. The specific diffuser type chosen depends on the desired airflow distribution.
- Sealing Pad: An additional layer of protection between the HEPA filter and the housing, further enhancing the overall seal.
- Duct Flange: The connection point for the HEPA box to the cleanroom's air handling system.
- Perforated Plate: An optional component that can be used to distribute airflow more evenly within the housing, particularly beneficial for larger HEPA filters.
- Hanging Holes: Facilitates the secure mounting of the HEPA box within the cleanroom ceiling grid.
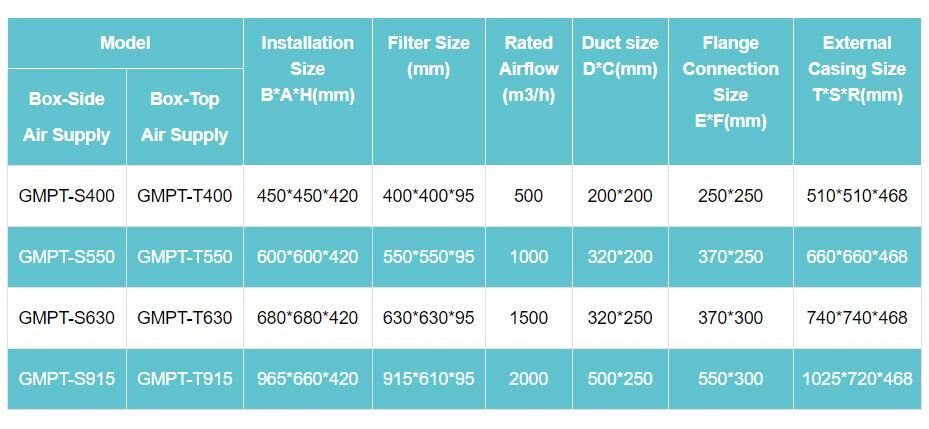
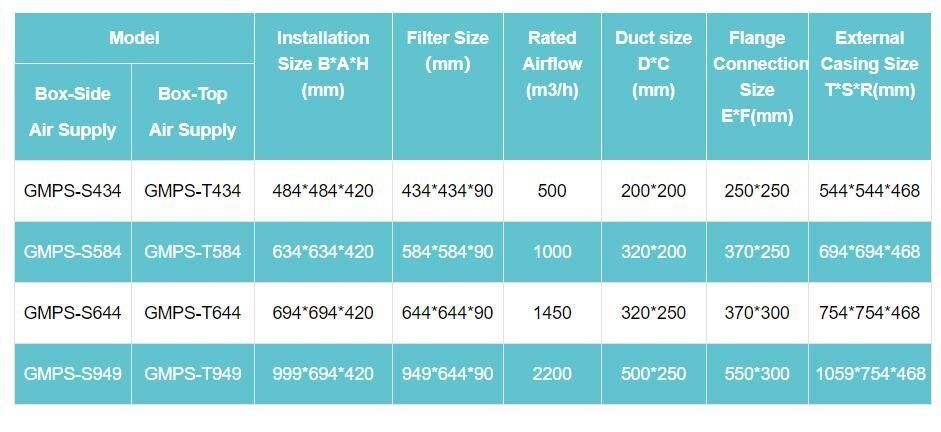
See more: Verifying HEPA Box Performance for Cleanroom Suitability
Top- Versus Side-Supply HEPA Boxes
As the provided note highlights, gel-seal HEPA boxes can be configured with either a side-mounted or top-mounted air supply. This flexibility allows for adaptation to various cleanroom layouts and airflow requirements. The optimal configuration depends on factors such as ceiling height, room dimensions, and the desired airflow pattern.
Conclusion
HEPA boxes with gel-seal technology offer a superior solution for pharmaceutical cleanrooms, guaranteeing the highest level of air purity and safeguarding product integrity. By understanding the components, functionality, and configuration options of these enclosures, facility engineers and cleanroom professionals can make informed decisions to ensure a controlled and sterile environment for critical pharmaceutical applications.
See more: HEPA Box Installation Best Practices